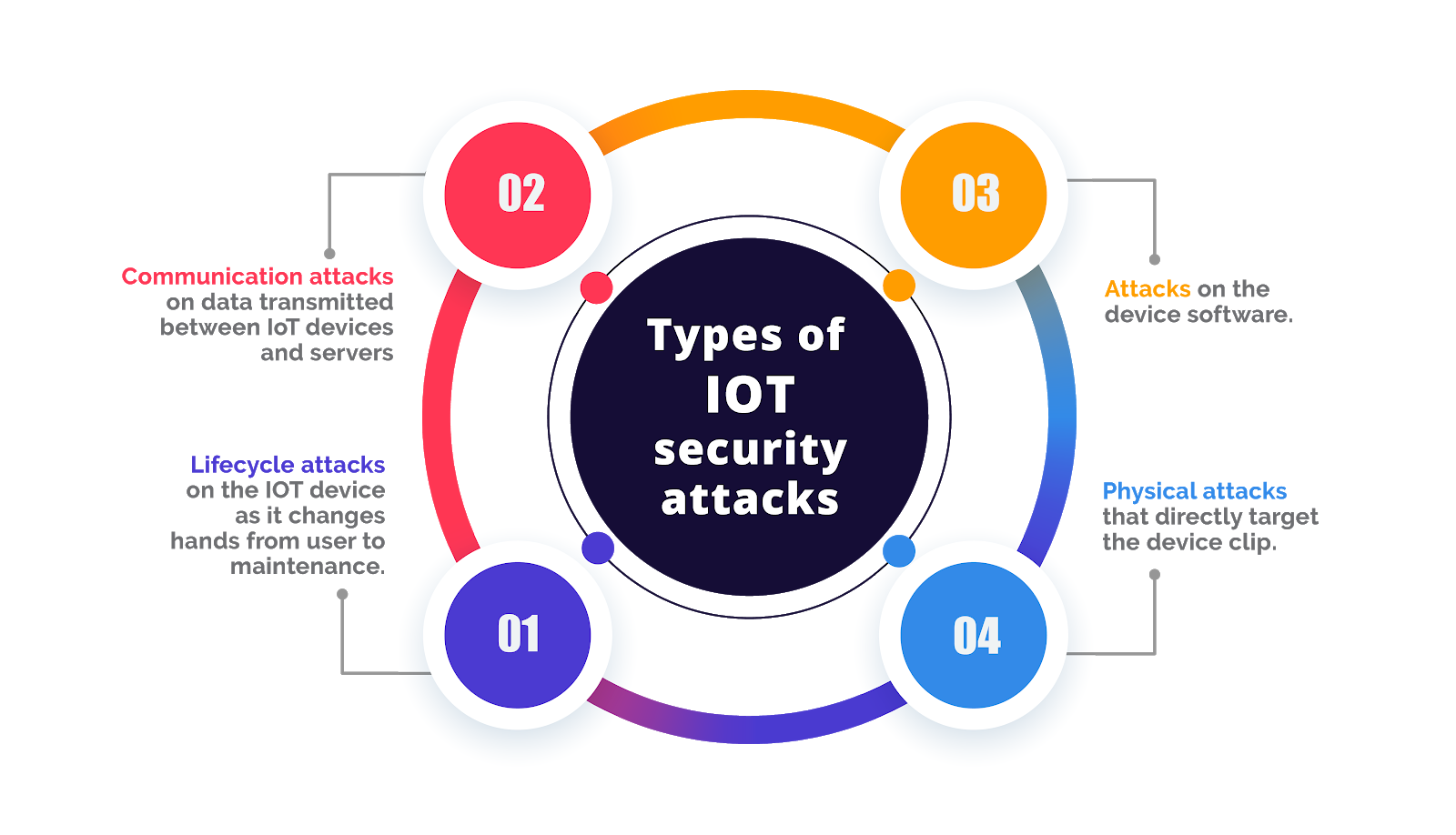
In an age dominated by interconnected devices, could your smart home, your car, or even your healthcare equipment be vulnerable to cyber threats? The reality is stark: the Internet of Things (IoT) is rapidly expanding, and its security is often lagging, creating a fertile ground for cyberattacks that can have profound consequences.
IoT security, a critical and often underestimated facet of cybersecurity, focuses on safeguarding the expansive network of interconnected devices that define our modern world. These devices, ranging from smart appliances and wearables to industrial sensors and autonomous vehicles, are designed to collect, share, and process data, often without robust security measures in place. This interconnectedness, while offering unprecedented convenience and efficiency, also introduces a multitude of vulnerabilities that cybercriminals are eager to exploit. The act of protecting these devices and ensuring they don't introduce risks into a network is known as IoT security.
The importance of IoT security cannot be overstated. As more and more aspects of our lives become reliant on these devices, the potential impact of a security breach grows exponentially. A compromised smart thermostat could disrupt your home's climate control, while a hacked connected car could pose a serious safety risk. Industrial IoT devices, controlling critical infrastructure, are even more appealing targets for cybercriminals seeking to cause widespread disruption.
| Aspect | Details |
| Definition | A cybersecurity practice dedicated to protecting IoT devices and networks from cyber threats, unauthorized access, and data breaches. |
| Key Components |
|
| Objective | To ensure IoT ecosystems remain secure and resilient against evolving cyber risks. |
| Core Functionality | Safeguarding interconnected devices (e.g., smart home devices, smart watches, security cameras, etc.) |
| Methodology | Cybersecurity strategy and protection mechanisms to protect against cyberattacks targeting physical IoT devices. |
| Essential Frameworks |
|
| Example of Implementation | Network segmentation: keeping IoT devices on a separate network to limit potential damage if one gets compromised. |
| Relevant Technologies |
|
| Data Management | Maintaining security, privacy, and integrity of data in storage (on the device, network server, cloud, etc.) and during transit. |
| Threats Addressed |
|
The landscape of IoT security is multifaceted. It encompasses a broad spectrum of technologies, strategies, and best practices aimed at mitigating the diverse threats facing interconnected devices and networks. It is based on a cyber security strategy of best practices to protect insecure iot devices and the vulnerable networks they connect to from cyber attacks. At its core, IoT security is a subsect of cybersecurity that focuses on protecting, monitoring and remediating threats related to the internet of things (IoT) the network of connected devices equipped with sensors, software or other technologies to gather, store and share data via the internet.
IoT devices are the weakest links in the network because they are everywhere. These include the likes of smart home devices, smart watches, smart door locks, networked security cameras, autonomous connected cars, voice control devices, smart healthcare devices, and more.
IoT security can be understood as a cybersecurity strategy and protection mechanism that safeguards against the possibility of cyberattacks which specifically target physical IoT devices that are connected to the network. Iot security is a threat protection mechanism and cybersecurity strategy that defends iot devices connected to a network against cyberattacks. The goal is to ensure the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of data generated, transmitted, and stored by these devices.
One of the first steps in establishing a robust IoT security posture is building a comprehensive asset inventory. Automated discovery tools can identify authorized and rogue devices, cataloging details such as device type, firmware version, network segment, and owner. This provides a clear picture of the organization's attack surface, enabling more effective risk assessments and mitigation strategies. Data security must be implemented throughout the entire IoT lifecycle across all devices and equipment, with a core aspect being to maintain security, privacy, and integrity of data in storage, and also during transit.
Organizations must not only address the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access but also manage challenges like distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks that can overwhelm networked devices in real time. A common example of IoT security is network segmentation keeping IoT devices on a separate network to limit potential damage if one gets compromised.
The implementation of IoT security is not without its challenges. IoT devices use a wide variety of protocols, operating systems, code languages, and hardware, which can complicate security. Older devices, in particular, may have inherent vulnerabilities that are difficult to patch or mitigate. Furthermore, the sheer volume of devices and the complexity of their deployment can make comprehensive security management a daunting task.
The internet of things (IoT) is one of the most widely used technologies today, and it has a significant effect on our lives in a variety of ways, including social, commercial, and economic aspects. In terms of automation, productivity, and comfort for consumers across a wide range of application areas, from education to smart cities, the present and future IoT technologies hold great promise.
Organizations need to follow recognized frameworks that outline best practices for IoT security. The NIST IoT Cybersecurity Framework provides detailed security guidelines.
IoT security breaches and success stories provide valuable lessons. Experiencing security incidents of IoT devices has taught organizations lessons about how to create their protection. The following case is a perfect example of security failures and success stories where strong IoT security practices were applied to mitigate them. Blindly adding IoT devices without security measures is asking for trouble.
The IoT security essentials (I|SE) is a comprehensive guide to securing the internet of things (IoT) systems. It covers essential topics from IoT fundaments to advanced security threats and security engineering, providing the knowledge and skills to design, deploy, and maintain secure IoT solutions.
The field of IoT security is constantly evolving, requiring organizations to stay ahead of attackers. Technologies such as those offered by Crowdstrike and SentinelOne, can protect IoT devices and networks from cyber threats.